Driving Innovation and Creating Value in a Competitive Industry
Since the development of the first semiconductors, the electronics industry has benefited from one groundbreaking innovation after another. As the cost of raw materials for chips, fiber cables, circuits and other critical electronics components falls, manufacturers have turned to next-generation robotics solutions to enhance operational efficiency and reduce labor costs without harming the quality and precision of finished equipment. Kawasaki Robotics has leveraged advancements in miniaturization and production speed to develop flexible, precise automation solutions for a variety of electronics applications.
Efficient Production, Consistent Results
Kawasaki Robotics' multi-position robots leverage human-quality dexterity to stamp, etch, press and handle small, lightweight semiconductor electronic components. Since they can be moved to multiple positions along the production line, they can easily execute component and final assembly tasks for consumer electronics like microwave ovens, desktop and laptop computers, mobile devices and location-finding systems with precision that far exceeds the capabilities of human workers. Meanwhile, their next-generation machine vision and sensing capabilities make Kawasaki robots ideal for inspection and quality control processes. After assembly, our flexible robots expertly palletize and pack sensitive equipment for delivery while disposing of leftover materials. Kawasaki's solutions augment every facet of the electronic assembly process.
The pace of electronics innovation continues to accelerate. As new opportunities emerge for manufacturers of RFID, handheld communication devices, broadband connectors, system-on-chip applications and other promising technologies, Kawasaki Robotics promises to develop flexible, precise automation solutions for an interconnected future.
Applications
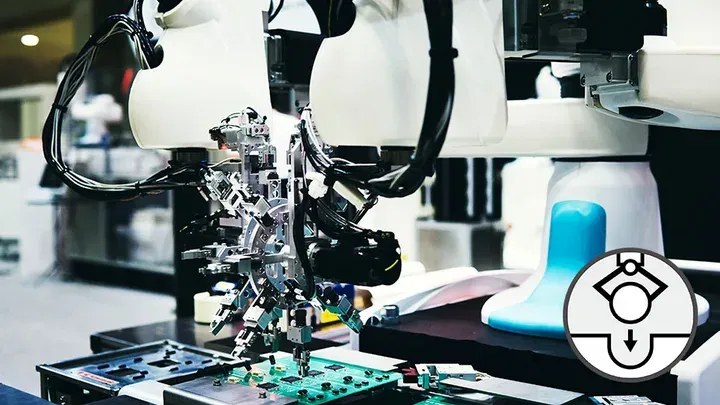

Assembly
The process of combining multiple parts to make components or products, assembly is performed in various manufacturing sectors, including machinery, electronics, and electrical sectors.
Assembly covers various tasks, including assembly of small precision parts and large and heavy workpieces.

Material Handling
The process of moving materials, parts, and products from one place to another, material handling is performed in almost all industries, not just in the manufacturing industry.
For material handling, industrial robots are most commonly used for various purposes, including high-speed transport of small parts and handling of heavy objects that humans cannot carry.

Machine Tending
A critical process in the machinery industry, machine tending involves loading parts into NC machine tools and unloading them after their machining is complete. Loading and unloading processing materials into and out of forging and press machines are also classified as machine tending.
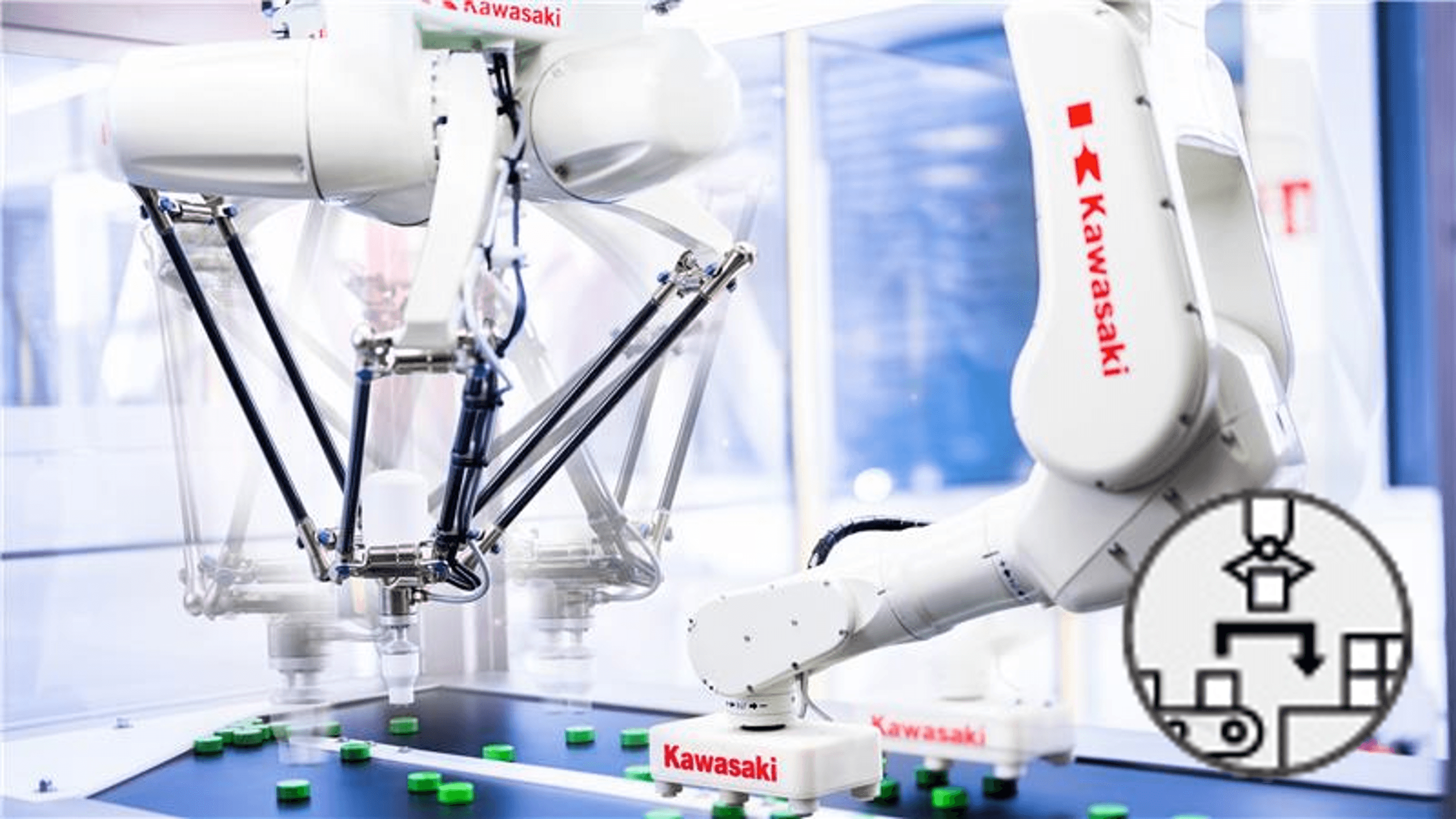
Pick & Place
Picking, also known as “pick and place,” is the process of grabbing workpieces from a conveyor belt and sorting them at high speed.
For this purpose, uniquely shaped robots called the parallel link type (or delta type) are used.
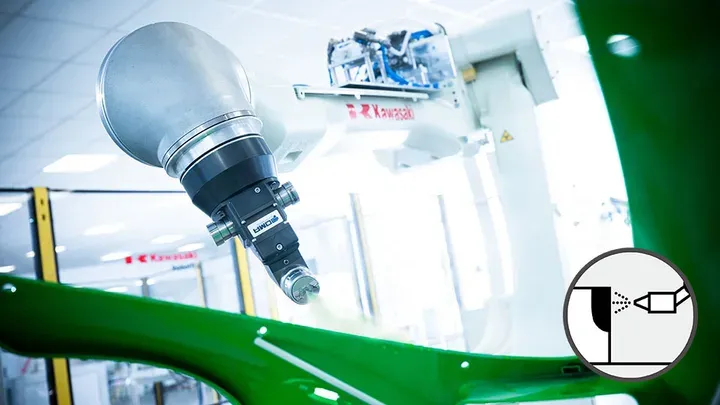

Painting
Painting is the process of applying paint on product surfaces, forming a coating film or finish.
Because most paint materials are highly volatile, explosion-proof robots and painting equipment are used for this process.
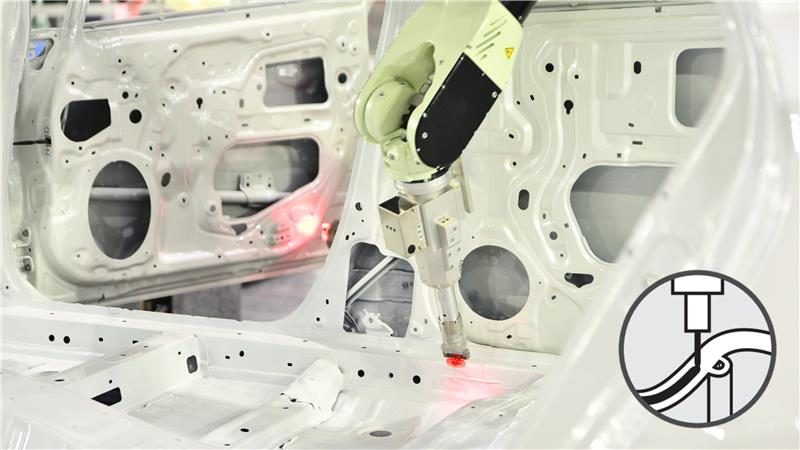

Sealing / Dispensing
Sealing is the process of applying sealant or adhesive to enhance airtightness and fill the space between materials.
Sealing is performed for many products, such as passenger vehicles and home appliances.
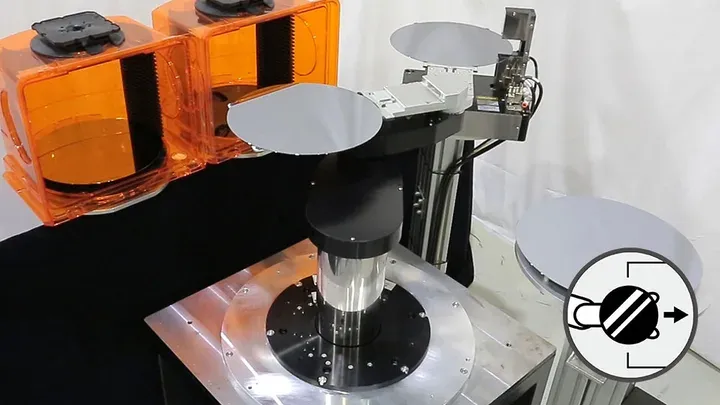

Silicon Wafer Handling
Wafer transfer is the handling of wafers in the front-end process of semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
This process uses clean robots and requires high-precision, high-speed and smooth movement.