Society has been expanding its expectations of the role robots play, looking at them to combat issues such as a declining population due to an aging society and frequently occurring natural disasters.
Collaborative robots (cobots) are attracting the attention of industries—some can coexist and work in the same space as humans, and others cooperate with humans working on the same operations. With robots helping take over tasks physically demanding on humans, or supporting humans in an operation, new approaches in how humans and robots work together and new social systems are gradually appearing.
Kawasaki Heavy Industries, or Kawasaki, whose robotics business has a history dating back over 50 years, is a leader in the field of industrial robots used on manufacturing lines in factories. The company is also dedicated to the development of cobots. With a lineup including duAro, a collaborative, dual-armed SCARA robot able to work alongside humans in a shared space, and the Successor robot system, which enables human-robot collaborations through the remote controlling of robots, Kawasaki is opening doors to new ways humans and robots can coexist with one another.
Looking forward into the future, Kawasaki has engaged in the development of humanoid robots. In 2017, the company unveiled a humanoid robot named Kaleido. Since then, there has been ongoing development to make this robot practical in human society, for example, in nursing care or sites affected by natural disaster.
The state of that progress was revealed at the International Robot Exhibition (iREX) 2019, held at Tokyo Big Sight between December 18 and 21. This article introduces the intentions behind Kawasaki’s development of humanoid robots, and the passion it has toward Kaleido.
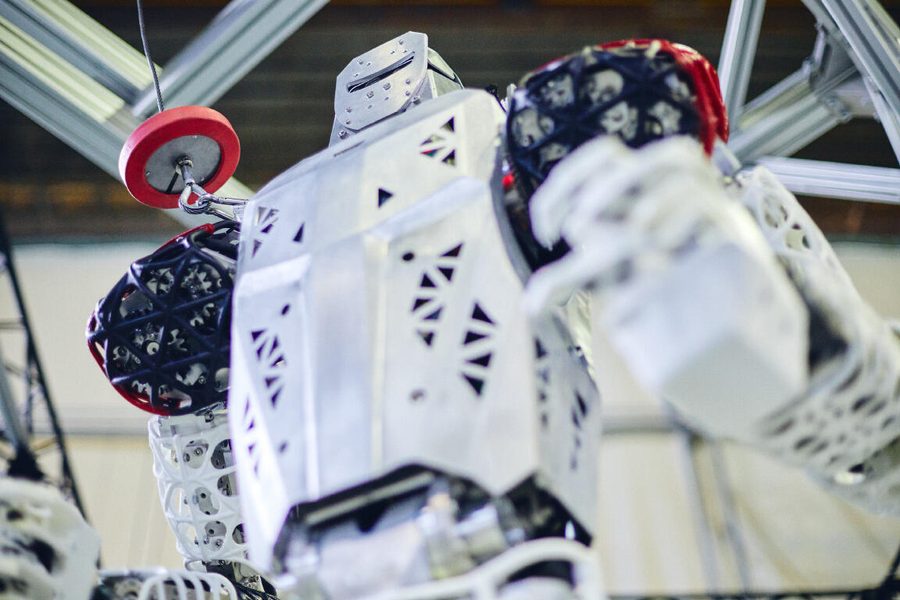

The humanoid robots Kawasaki develops
Kawasaki has manufactured robots for 50 years. Why does a company that mainly manufactures industrial robots used in factory production lines work on the development of humanoid robots? Yasuhiko Hashimoto, President of Precision Machinery & Robot Company, explains.
* The interview took place before iREX2019 started.

“Unfortunately, Japan is behind in the development of humanoid robots today compared to other countries. When we asked the researchers about why that is, they said that it is because most of their research time is spent repairing and maintaining the robots.
The researchers are hoping to develop a robot that will never fall over. However, similar to raising children, if humanoid robots are not allowed to jump because it is deemed to be too dangerous, then they will never master how to jump.
But, if there were parts available that would not easily break, it would make such a challenge possible. If there is someone around who can repair any damage done, then we can let robots jump without worrying. We want to change the conservative attitude of not trying to take on new challenges by providing durable humanoid robots. We want to establish an environment that would allow breakthroughs.” (Mr. Hashimoto)
Kawasaki is among the top five industrial robotics companies in the world, and the knowledge and expertise it has acquired through providing solid, reliable robots in order to avoid interruptions in manufacturing, is put to use here.
Even for researchers, having robots that do not fail even after a fall is very important to the continuation of their research. Check the article linked below detailing the importance of solid hardware as pointed out by Professor Masayuki Inaba of the University of Tokyo, who is involved in the collaborative research effort, and what sparked the joint project between Kawasaki and the University of Tokyo.
Exploring Robots’ Future with the New Model of Humanoid Robots
Humanoids are the ultimate form of robots that coexist with humans
Now, if a future where humanoid robots coexist with humans were to happen, what kind of benefits would humanoid robots bring to our everyday lives?

”The industrial robots that are already in use today are like specialists that handle precision tasks while working in an restricted environment, such as on a production line or on top of a worktable. In contrast, the environments people live in change every day.
Robots must be able to go to places where people go if they are to be useful in a human society. That is why we are very particular about making our humanoid robots the same size as an adult male.
The ability to lift up objects weighing the same as its own body is also important. Humans can do this even if just for a second, so if this becomes possible for robots, then they will be able to handle the same tasks humans do.
Take, for example, disaster rescue and relief situations and nursing. Robots can perform rescue operations in dangerous environments where there is a possibility of secondary disasters. And in nursing, where on-site support is required around the clock, they will be able to assist those providing care to patients; it will reduce the burden on both the caregivers and those who receive care. We want robots to take over tasks that are physically hard for humans.
Buildings and towns are designed with a focus on the human body. Moving forward, robots are going to be expanding their roles and coexisting with humans, and in order to make that happen, the ultimate appearance of robots should be human-like. By having robots resemble humans, it will allow them to be all-purpose workers, no matter what kind of environment they are in.
We have also been hearing many industries express their expectations of humanoid robots these days. In the past, work environments had to be configured if a specialized robot was used for certain operations. This could have meant doing things like individually systemizing operations in order to accommodate that robot. However, with humanoid robots, they can work in a hospital if they simply put on a white coat or serve as a firefighter just by gearing up in a firefighter’s uniform.” (Mr. Hashimoto)
Well then, how close currently is Kaleido to its ideal form?
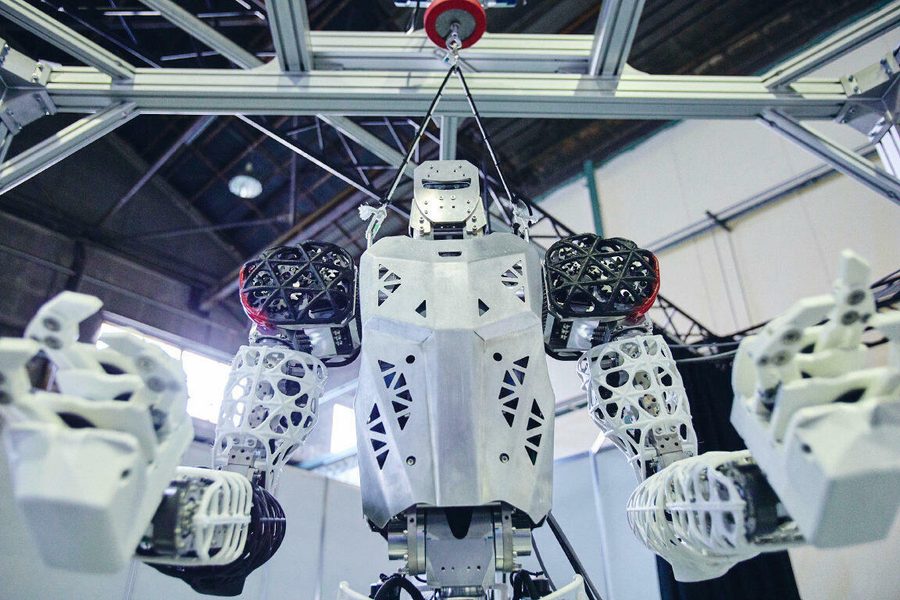
” Having introduced Kaleido on various occasions, we believe we have reached the point where people are excited and inspired by it. It undoubtedly stands at a high level even among other humanoid robots in the world today.
However, in terms of how useful it is for humans, we have only stepped on the starting line. Kawasaki continues to pursue and improve upon robotic hardware that is more flexible and durable than ever before. And with regards to developing applications that work for different usage scenarios, we hope to bring up our humanoid robots with the support of researchers around the world.
Our Kaleido will demonstrate a disaster rescue operation as an example of how it can help humans during the iREX2019. We hope that the potential Kaleido holds will draw the interest of people from all over the world.” (Mr. Hashimoto)
Humanoid robots continue to evolve as a platform that can take on challenges. The article linked below recounts how the humanoid robot has progressed in capabilities since its debut in 2017 to the present. Don’t miss it.
Two Years On from Its Debut, How Kawasaki’s Robust Humanoid Robot Evolved