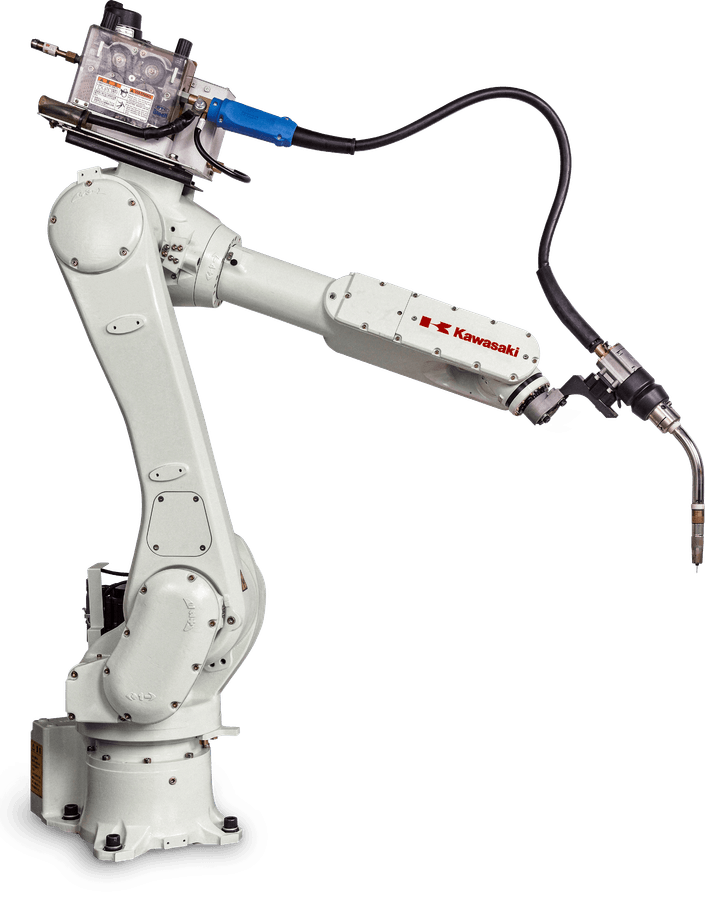
Arc Welding
Robots
What is Arc Welding?
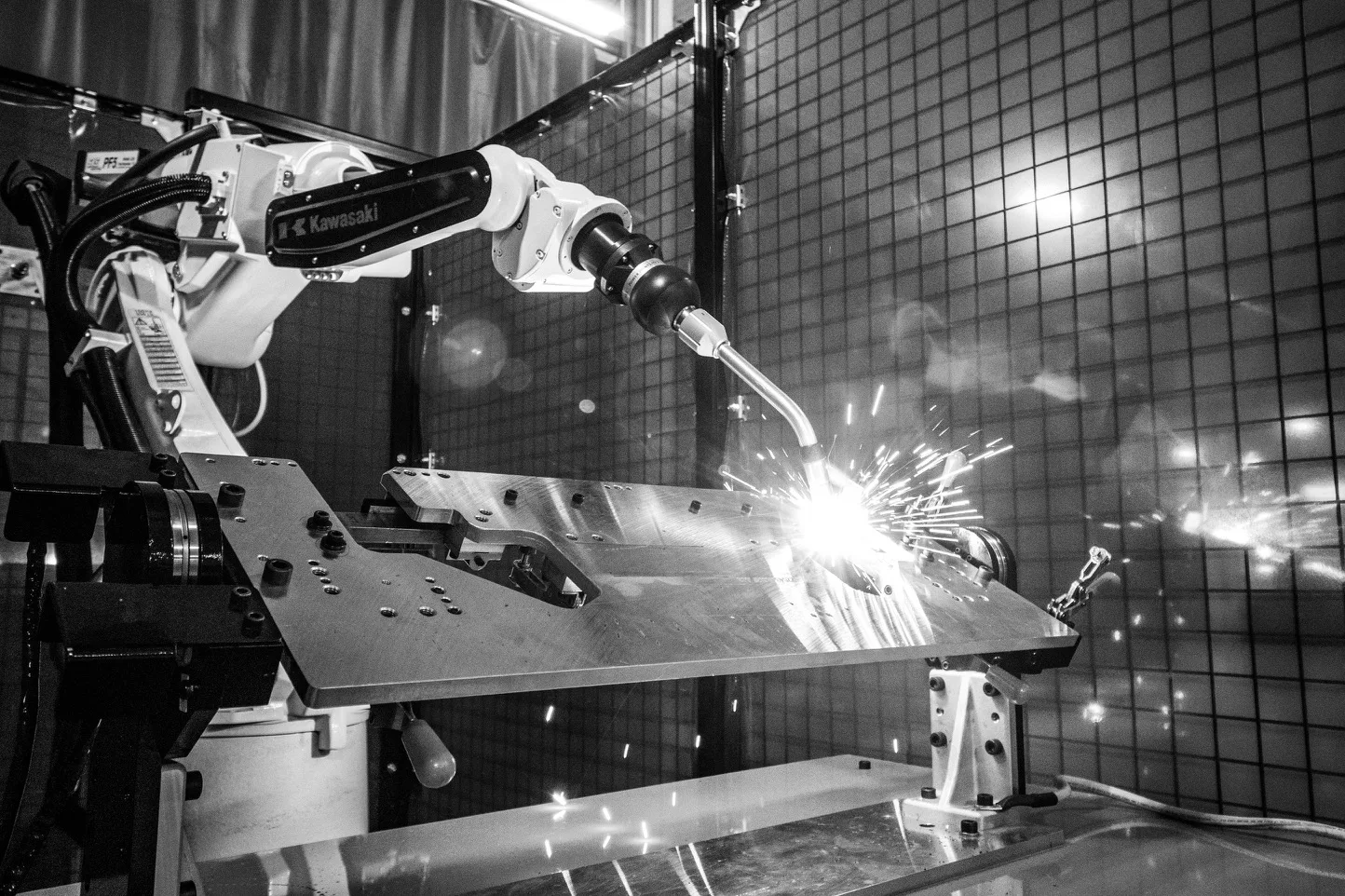
Arc welding is the process of joining metals using the heat generated from an electric arc, and this can be done using different techniques such as MIG (Gas Metal Arc Welding), TIG (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), PAW (Plasma Arc Welding) and more. It is a go-to method for anyone working with metal, whether in the automotive industry, construction or industrial equipment manufacturing.
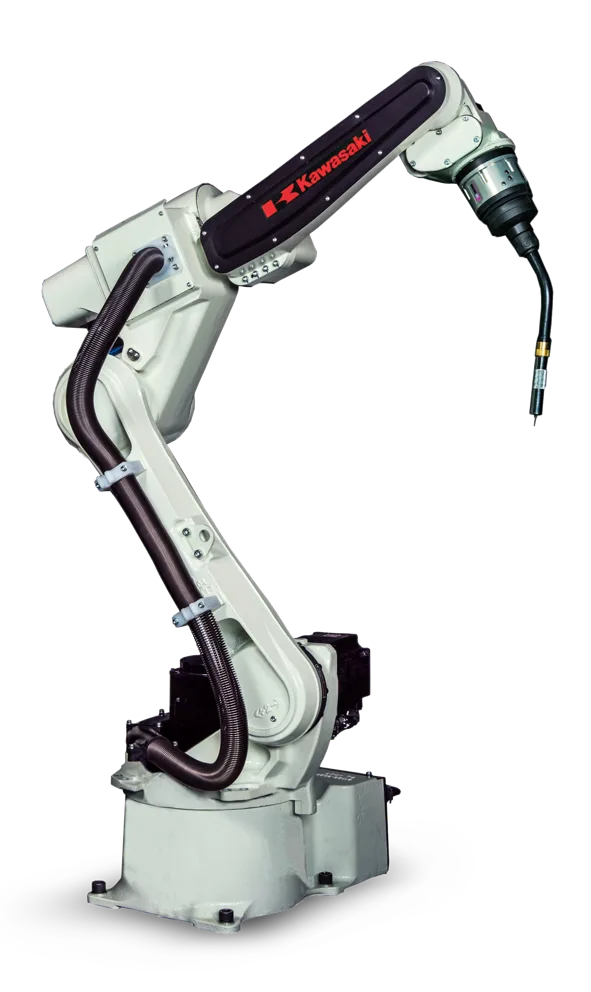
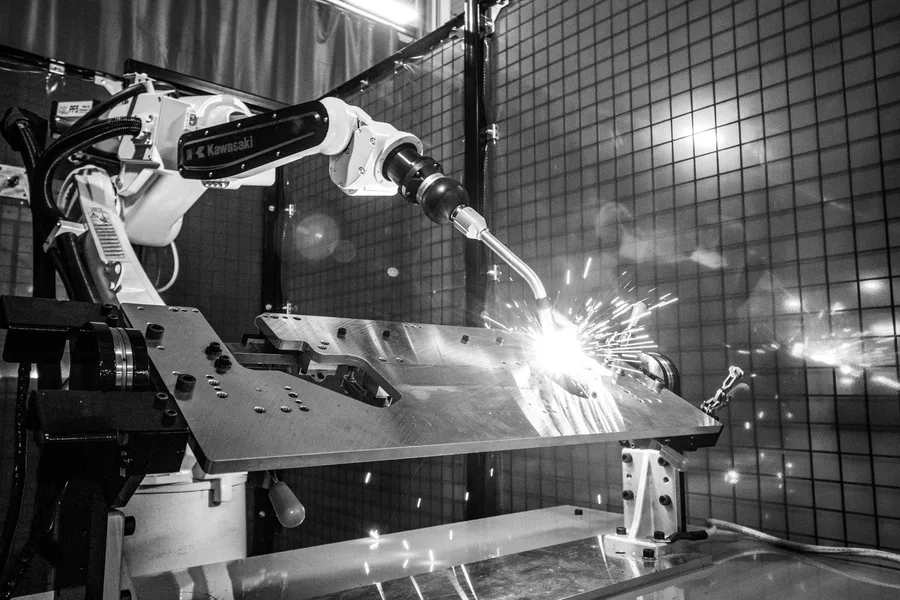


How Manufacturing Companies Can Overcome ARC Welding Challenges
One of the major challenges today is the shortage of skilled welders; the American Welding Society (AWS) projects that 330,000 new welding professionals are needed by 2028 with 82,500 average welding jobs to be filled annually between 2024 and 2028 in the United States to meet the increasing demands from industry sectors such as infrastructure, energy, automotive and construction.
Now combine that with rising and constantly fluctuating material costs, supply chain disruptions and the need for customization and part flexibility, and it comes as no surprise that keeping production costs down and profit margins up is a major challenge. Technological advancements—such as automation and advanced manufacturing processes—are needed in order to stay competitive. However, navigating this landscape can feel daunting, considering it requires time, investment and training.

The Kawasaki Robotics Difference
Since the 1960s, Kawasaki Robotics has been at the forefront of robotic arc welding technology, continuously refining our solutions to meet the evolving needs of manufacturers. Our decades of innovation have helped businesses simplify the adoption of automation, overcome labor shortages, and keep pace with increasing customer demands and shifting market conditions.
Powerful & Flexible Welding Solutions
Kawasaki arc welding robots are designed to integrate seamlessly with any major welding power supply, giving you flexibility and control over your production environment. We also provide a full range of modular K-Positioners and K-Tracks, along with advanced features such as:
- Start sensing for accuracy
- Touch sensing for precision joint location
- Adaptive fill technology for consistency
And the best part? These features come standard.
To ensure your long-term success, we back every project with comprehensive through-life engineering services, training, and dedicated support.
Collaborative Robot Weld Packages — Starting at $75,000
Looking to make welding automation more accessible?
Our new collaborative robot weld packages start at just $75,000. These solutions are designed to lower the barrier to entry, making high-quality robotic welding achievable for shops of all sizes. With easy deployment and safety-focused designs, our cobot welding packages allow you to boost productivity without heavy upfront costs.
Technology Partnerships That Drive Success
Another advantage of working with Kawasaki is our strong network of integrators and technology partners. Our technology-agnostic approach ensures compatibility with a wide range of welding solutions and software, so you get the exact system you need. Whether it’s:
- Adaptive laser vision for real-time joint tracking, or
- Post-process weld inspection to guarantee quality,
Our partnerships remove barriers to adoption and deliver results you can rely on. By combining Kawasaki’s advanced arc welding technology with the expertise of our partners, we create fully customized solutions that deliver the quality, speed, and efficiency today’s manufacturers demand.
Our Arc Welding Robots
(and What Makes Them Special)
Using open architecture and state-of-the-art technology, our line of arc welding robots fully match the quality of a skilled welder. Address labor shortages, meet production goals and improve quality.
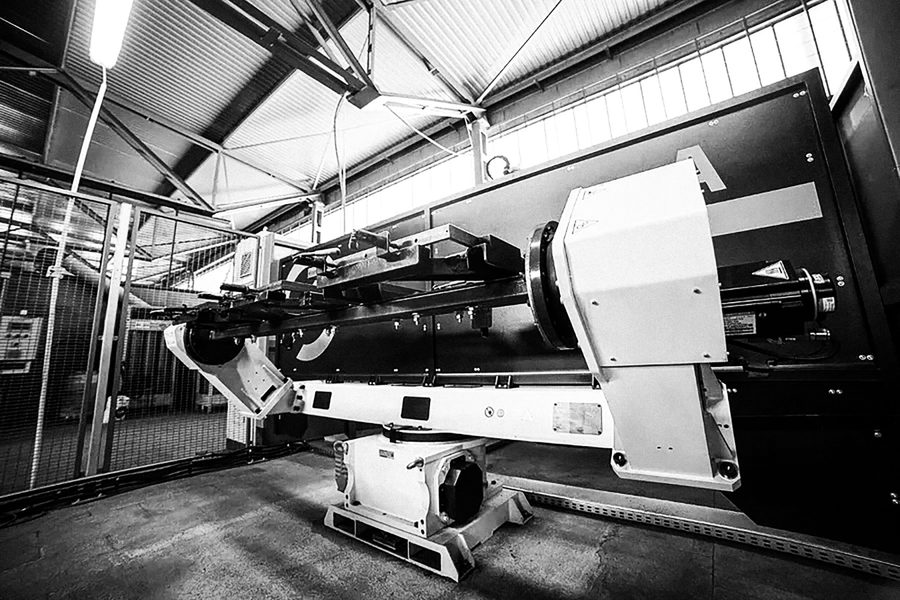

MAXIMUM WELDING PRECISION AND SAFETY
We offer a line of single-axis and multi-axis positioners, which are able to manipulate products up to 3000 kg. All are available in standard configurations or customized to fit your needs. The modular construction of K-positioners makes it easy to modify or adapt them as needed.
K-Tracks linear tracks extend the working range of our robots. They are available in various standard configurations or can be customized according to your needs.
Thanks to our software suite, arc welding robots, technology-agnostic stance and partner network, we make it remarkably easy to build your complete welding solution—whether you are an expert in automation technology or a novice user.