1/1 Pages
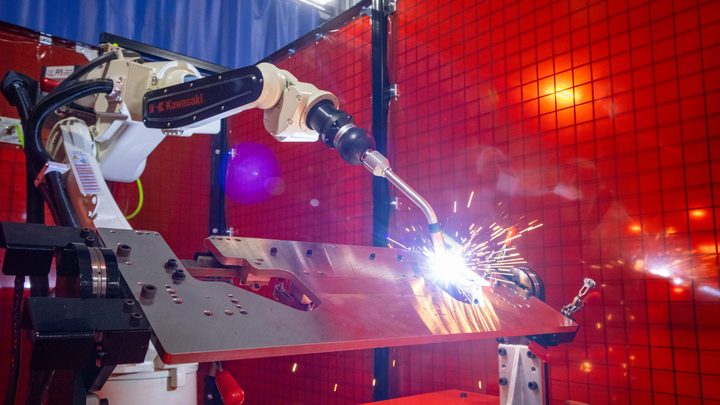

Robot integration in many welding applications makes sense, given that welding is not conducive to pleasant working conditions for humans. Not only is it a hot and dirty process, but it also emits unhealthy chemicals such as…

Kaggle, a global AI data analysis competition platform, hosted the National Football League (“NFL”) and Amazon.com, Inc. […].
Industrial robots were born to perform laborious tasks for humans, including repetitive, dangerous processes and handling heavy objects, among others. Initially, robots were implemented for the automotive industry, but they have since expanded to others, including machinery and appliance manufacturing, agriculture, forestry, civil engineering, medical/pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics industries — and more. Robots have proven to be particularly useful for lines with short product cycles, small-lot production of goods, and mixed-quantity production. As these needs are increasing, robots’ abilities are expanding. But when it comes to actually implementing a robot, a lot of questions arise. “What tasks can you leave to the robot?” “What steps do I need to take?” […]
