Assembly
Robots
WHAT ARE ASSEMBLY ROBOTS?
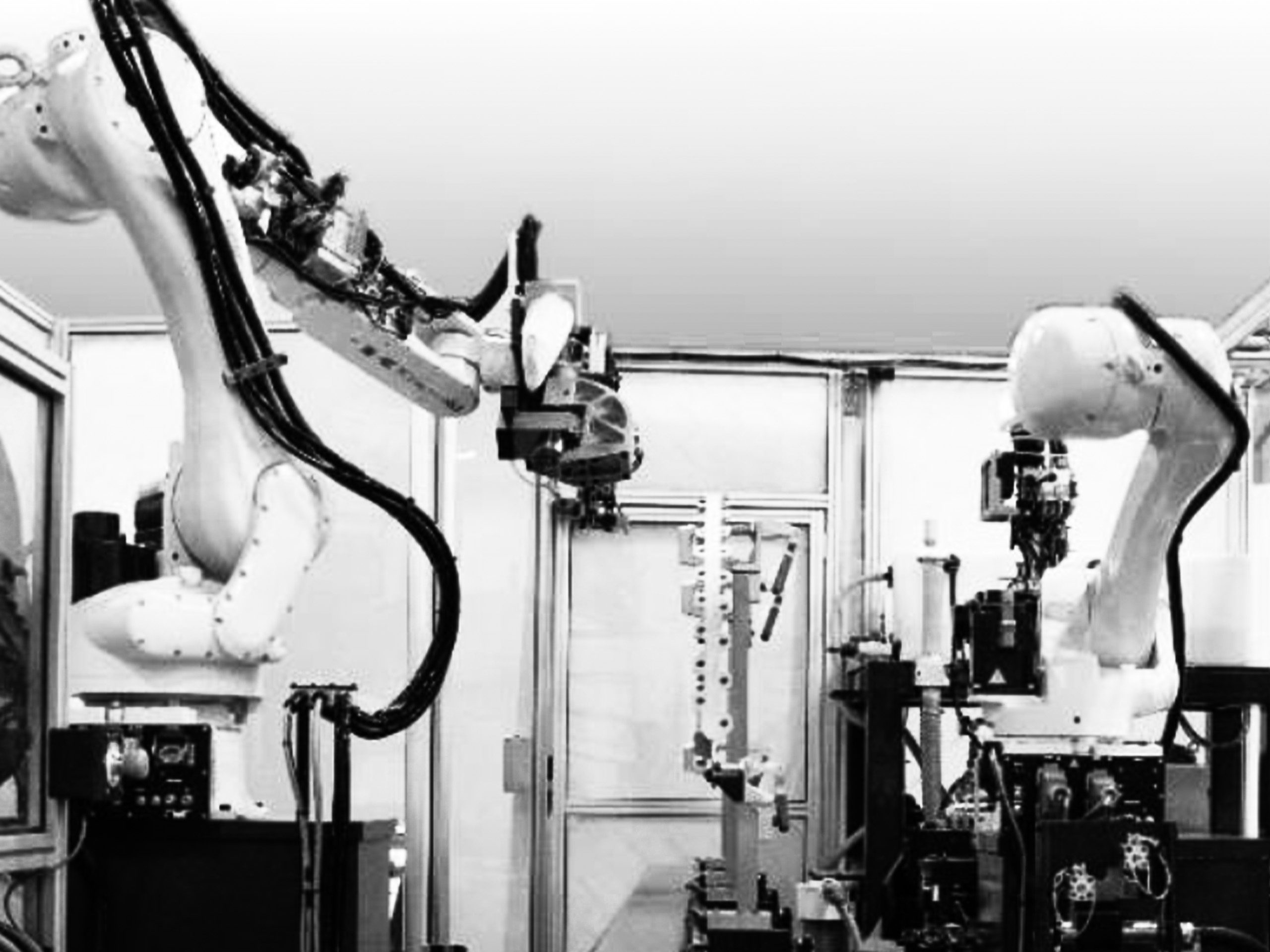
In manufacturing, robotic assembly refers to using robots to automate the process of assembling components and products. Thanks to advances in automation control technology, robots can today complete complex assembly processes previously deemed impossible.
Robotic assembly is commonly deployed in industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and more. However, the benefits are not limited to a single sector, but are applicable across various industries, making robotic assembly a valuable application for manufacturing.
Assembly robots, unlike human workers, do not need to take a break and can perform repetitive tasks without fatigue. Moreover, the precision and accuracy of assembly robots contribute to better product quality and fewer defects, further enhancing their efficiency in the manufacturing process.

THE CHALLENGES OF
assembly APPLICATIONS
Whether your assembly operations consist of insertion (inserting plugs, pins, etc. into target holes or fittings), joining (bringing two or more parts together and securing them into a single part), or fastening (applying screws, fasteners, bolts,) etc. Automating your assembly process may seem daunting as it requires a high degree of accuracy, precision, and stability, as parts may vary in shape, size, and surface characteristics.
While a human can quickly understand the exact shape of a part and know exactly how to pick and join the parts, the increasing difficulty in finding humans willing and able to perform these repetitive tasks over a long period of time is a growing concern. This is not just a matter of throughput, but also a significant factor in part quality, making it urgent to address these labor challenges.
Automating the assembly process can be challenging; however, with the right technology partners, assembly robots can achieve accurate perception, motion, and coordination needed to perform assembly tasks.

The Kawasaki
Robotics Difference
For over 50 years, Kawasaki has been developing technology to meet the high demand of assembly applications, whether you are bin picking, inserting, joining, or fastening. Our technology-agnostic stance allows us to provide customers with the best solution and our commitment to through-life services make us a reliable partner.
The major differences arrive when you factor in our open source programming and surprisingly human support.
We’ve always had a manufacturer-first mindset, because we’re a manufacturer ourselves. Our open-source programming platform offers several types of programming languages for all skill levels, letting users easily scale from basic operations to AI integrations. This, combined with our exclusive online resources and tools, puts our customers and partners comfortably in the driver’s seat at all times.
And when you work with us, you won’t find hidden and costly surprises for added software capability, product manuals, training, remote service calls and more. We pick up the phone when you call, and we treat you the same whether you’re a large-scale enterprise or a small business. We speak plainly and we never mislead, always treating our customers and partners the way we would hope to be treated.
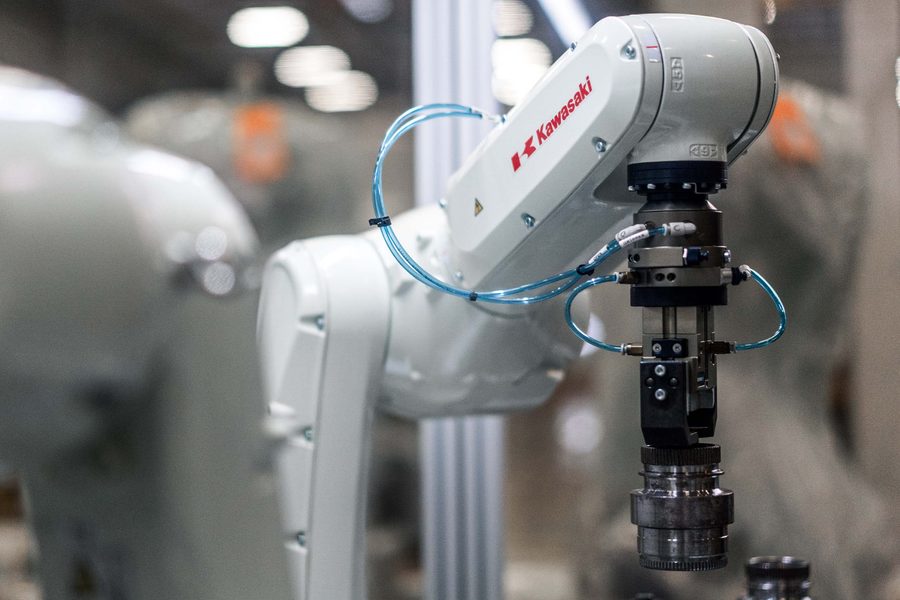

HOW WE DO ROBOTIC
ASSEMBLY DIFFERENTLY
Assembly applications demand a high degree of accuracy, precision, and stability. Kawasaki Robotics commitment is to provide the best solution possible to our customers and that means we are truly technology agnostic. This differentiator is especially important for assembly applications as meeting assembly requirements often require that machine vision is deployed.
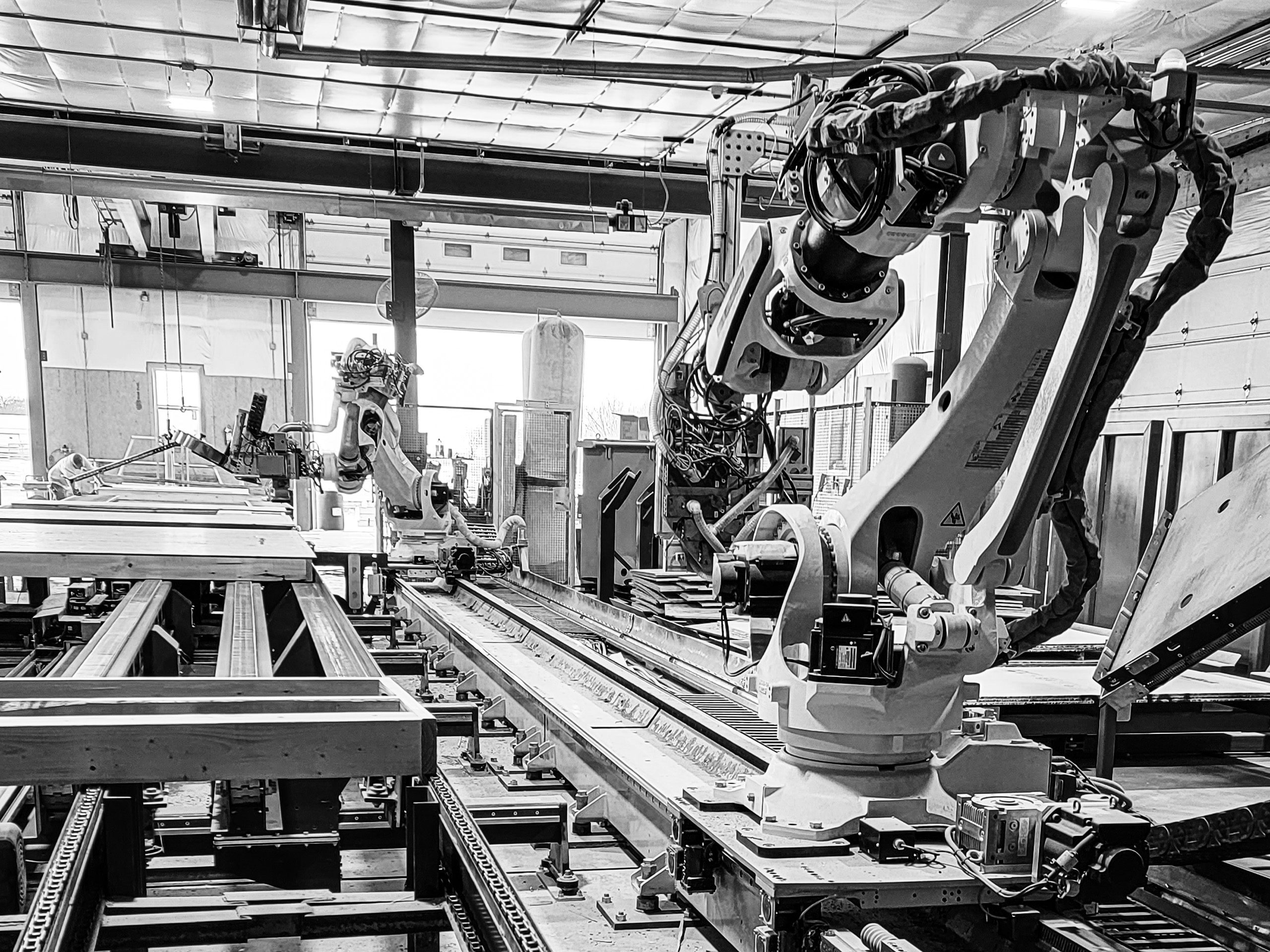
Kawasaki offers standard interfaces for inspection and motion guidance by 2D and 3D vision systems. These vision systems play a key role in locating specific parts, determining unique part characteristics, and identifying general part errors such as incorrect part orientation, missing or damaged parts, or part variations. Additionally, Kawasaki robots can be paired with force-compliance tools to ensure the end effector can adjust the force applied depending on the part, further enhancing precision.
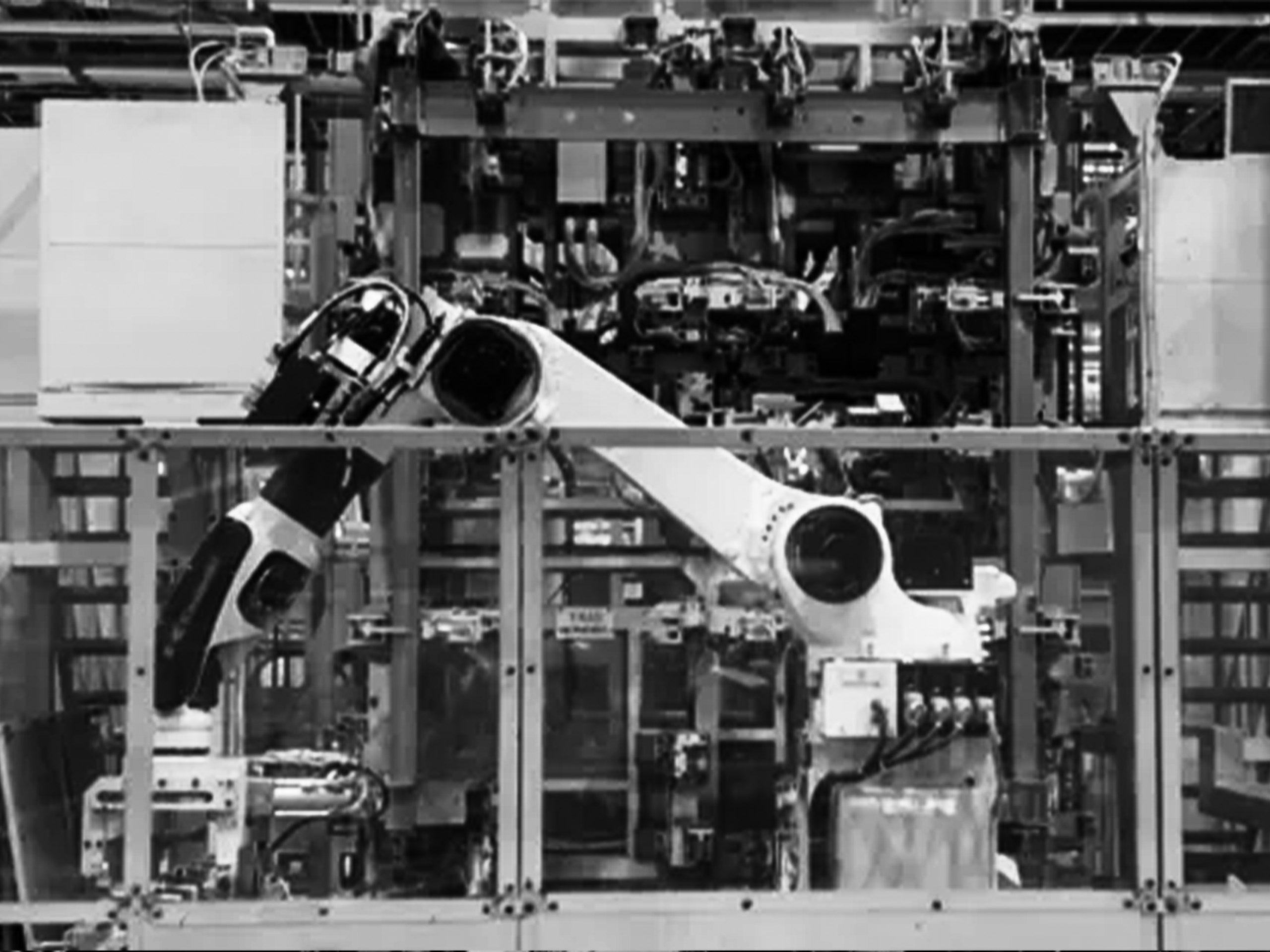
Multiple robots can be synchronized to lift or assemble a large component for large assembly applications using cooperative motion control. Servo end-of-arm tooling and multi-axis positioners can all be controlled by the Kawasaki robot controller to complete multiple assembly operations in a single work cell.
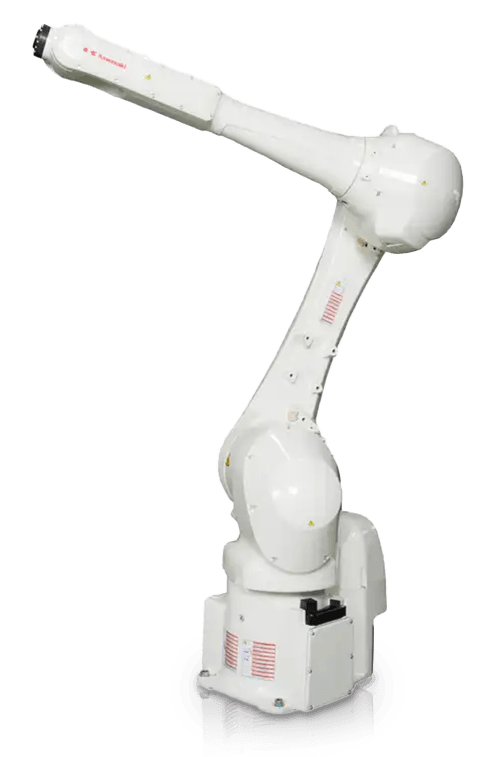
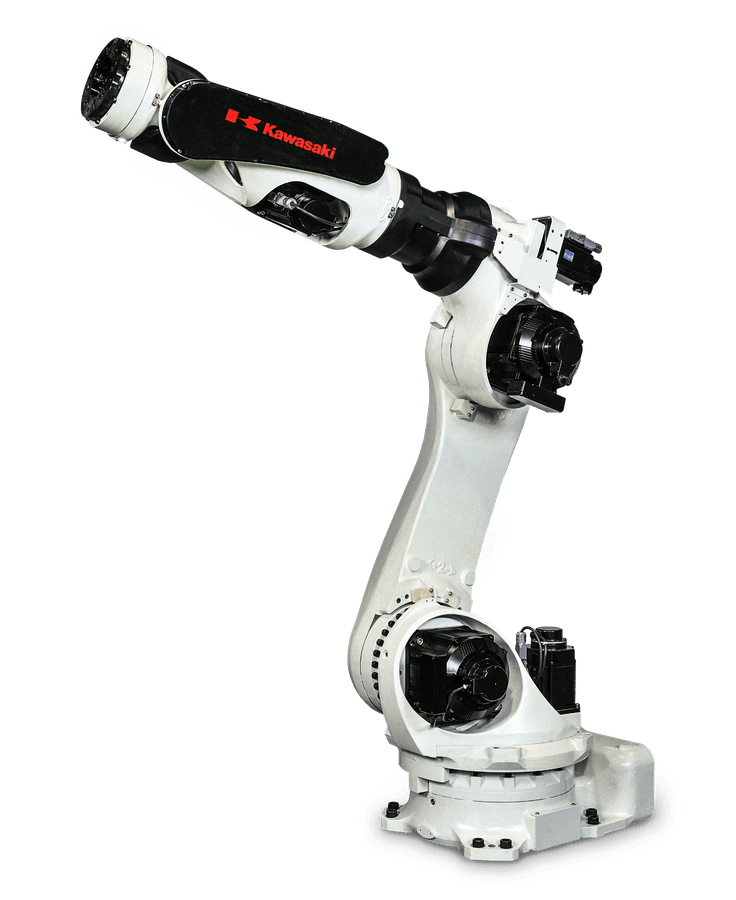
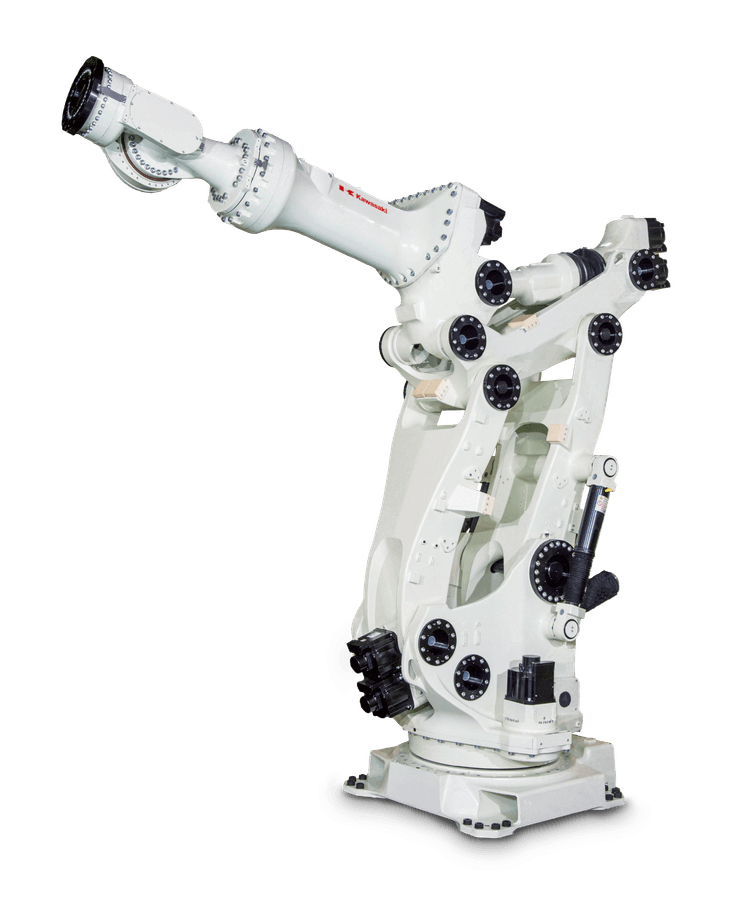
OUR ASSEMBLY ROBOTS
(AND WHAT MAKES THEM SPECIAL)
Our robots, paired with our open architecture software, allow us to be genuinely technology agnostic, which means we can select the best machine vision and end-effectors needed to complete assembly tasks while maintaining the highest standards of accuracy and precision.
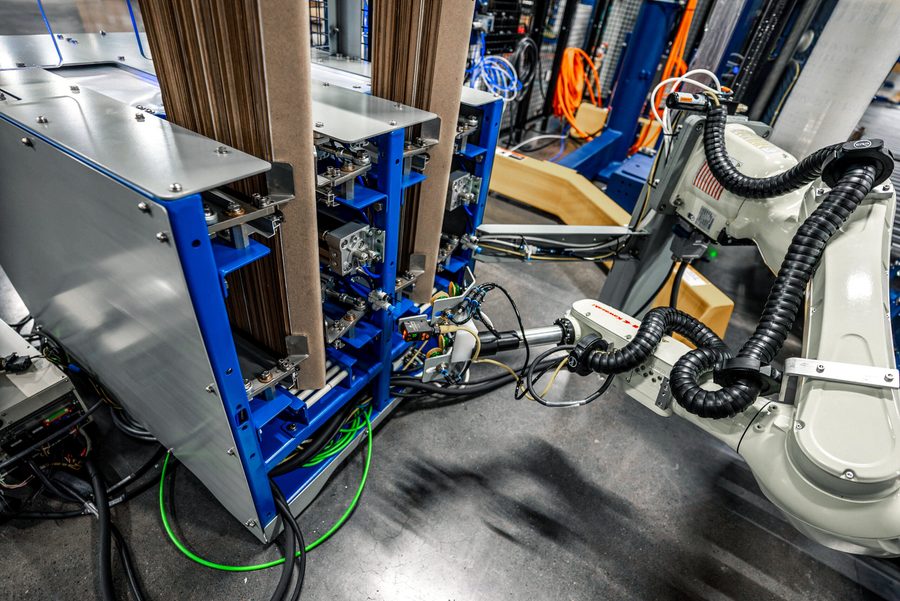
ASSEMBLY AUTOMATION IS BETTER WITH KAWASAKI
At Kawasaki Robotics, we don’t just sell hardware. We provide comprehensive through-life support and services, backed by our proven and productive hardware, open architecture software, and technology-agnostic stance. This level of support is a rare find in the industry, and it’s our commitment to ensuring your success.
Our extensive network of integration and technology partners allows you to harness the power of our comprehensive software suite. Whether you require a simple or complex assembly solution, our suite, which includes AI capabilities, has you covered. And the icing on the cake: Kawasaki has inventory available. All in all, you get industry-best lead times on delivery, followed by complete freedom to develop exactly as you want to.